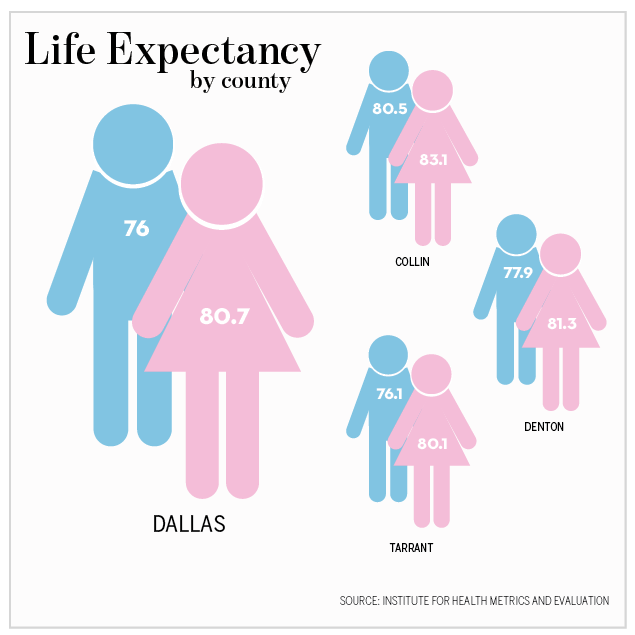
Life expectancy grew in two decades by more than seven years for Collin County men and about half that much for Collin County women. A recent report by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) found that the county closed the life-expectancy gap with the nation’s highest rate from about eight years in 1989 to about one year in 2009.
The nation’s highest life expectancy for men is Marin County, CA, at 81.6 years. Collin County men are not far behind at 80.5 years.
 The County Health Rankings, prepared by the University of Wisconsin Population Health Institute, ranked Collin No. 1 in Texas for health factors, such as health behavior, healthcare access, and social and economic factors. It ranked No. 2 in health outcomes, based on a low rate of premature deaths and lowest number of residents in poor health. No. 1 is Kendall County in the Hill Country, about 30 miles northwest of San Antonio.
The County Health Rankings, prepared by the University of Wisconsin Population Health Institute, ranked Collin No. 1 in Texas for health factors, such as health behavior, healthcare access, and social and economic factors. It ranked No. 2 in health outcomes, based on a low rate of premature deaths and lowest number of residents in poor health. No. 1 is Kendall County in the Hill Country, about 30 miles northwest of San Antonio.
Life expectancy tracks closely with household income. The affluent live longer. As of 2006, Collin was the second-richest county in Texas after Fort Bend, and one of the nation’s wealthiest. Twenty years ago, the county has begun its transformation from a rural enclave to explosive suburban growth. Its population tripled during those two decades, bringing in a high number of children and adult of child-rearing age. During the 1990s, Collin was the fastest-growing county in Texas and the 11th fastest-growing U.S. county. It fell slightly to the 13th fastest in the U.S. between 2000 and 2010.
Men in the other three metropolitan counties—Dallas, Tarrant and Denton—also made significant gains, though not as pronounced as those in Collin. Men gained about twice as many additional years of life as women in every county –though they still trail women in longevity by 3-5 years.
IHME researchers attributed male improvement to several factors: They are smoking less than past generations, are less likely to be obese than women, and are more likely to treat high blood pressure and high cholesterol. In the past, men tended to die earlier than women because of heart-related health risk factors. Heart disease has emerged as the leading cause of death for women, and more women than men die of heart disease annually.





